Hello Learners, Today we will learn the Advantages and Disadvantages of microcontrollers.
In this post, I will explain the microcontroller's benefits and limitations.
This Article is the Best on the whole internet.
I guarantee you, after reading this article, you will not need to read any other Articles. In fact, our readers are satisfied with this blog post.
Note – The only purpose of this article is to tell you about the pros and cons of microcontrollers in very simple language. This article has been written by an expert person. If you think this article can be improved further, then you must give us feedback.
What is a Microcontroller?
A microcontroller is a compact integrated circuit designed to perform specific tasks in embedded systems. It typically contains a processor, memory, and input/output peripherals devices all on a single chip.
Thanks to their small size and versatility, microcontrollers power devices ranging from microwave ovens to medical equipment.
Now, let’s break down the advantages and disadvantages of microcontrollers in detail.
Advantages of Microcontroller
Microcontrollers offer several significant benefits that make them a popular choice for a wide range of applications.
1. Compact and Lightweight Design
One of the biggest advantages of microcontrollers is their compact size. Since the CPU, memory, and I/O ports are integrated into a single chip, microcontrollers occupy minimal space.
Key points:
- Ideal for portable and space-constrained devices.
- Reduces the complexity of circuit design.
- Enables sleek and lightweight product designs.
2. Cost-Effective Solution
Microcontrollers are designed to be affordable, making them a great choice for mass-market products.
Key benefits:
- Lower development cost compared to building systems from discrete components.
- Perfect for cost-sensitive applications like consumer electronics and toys.
- Reduces the need for additional external hardware.
3. Low Power Consumption
Many microcontrollers are optimized for low energy consumption, which is essential for battery-operated devices.
Advantages include:
- Longer battery life for portable devices.
- Energy efficiency contributes to sustainability.
- Suitable for applications like smartwatches and IoT sensors.
4. Real-Time Processing Capabilities
Microcontrollers are excellent for real-time applications where quick and predictable responses are necessary.
Why it matters:
- Instant processing of sensor data.
- Critical for systems like medical devices, automotive controls, and robotics.
- Reduces the lag between input and output.
5. Easy to Program and Update
Modern microcontrollers support user-friendly programming environments and can be updated remotely.
Highlights:
- Availability of development tools like Arduino IDE, MPLAB, and Keil.
- Easy firmware updates enable improvements without hardware changes.
- Supports rapid prototyping and innovation.
Disadvantages of Microcontroller
Despite their many advantages, microcontrollers also come with certain limitations that designers must consider.
1. Limited Processing Power
While microcontrollers are suitable for simple tasks, they struggle with complex computing requirements.
Drawbacks:
- Not ideal for high-end gaming, data analysis, or artificial intelligence tasks.
- Limited clock speed and memory capacity restrict performance.
- Multi-threading and heavy multitasking are challenging.
2. Restricted Memory
Most microcontrollers come with a fixed amount of RAM and ROM, which can be a constraint in some projects.
Issues to be aware of:
- Limited memory limits the complexity of applications.
- Developers must optimize code and manage memory carefully.
- Adding external memory increases design complexity and cost.
3. Limited User Interface Options
Compared to full-fledged processors, microcontrollers often lack advanced graphics capabilities.
Challenges include:
- Difficult to implement rich user interfaces like touchscreen GUIs.
- Primarily suited for simple displays like LED screens or basic LCDs.
- Not ideal for multimedia applications.
4. Device-Specific Constraints
Microcontrollers are often tailored for specific tasks, which can restrict their versatility.
Important points:
- Harder to repurpose once embedded into a product.
- Hardware limitations can require complete redesigns for major upgrades.
- Integration of additional functionalities may demand external hardware components.
5. Vulnerability to Environmental Factors
Since microcontrollers are electronic computer components, they are sensitive to environmental factors such as heat, humidity, and electromagnetic interference.
Potential risks:
- Overheating can cause malfunction.
- Moisture and dust can damage circuitry.
- Shielding and protection add to overall design complexity.
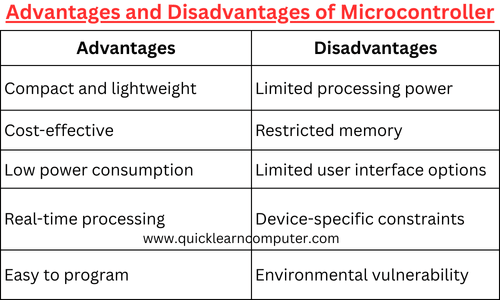
Summary Table: Advantages vs. Disadvantages of Microcontroller
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
Compact and lightweight | Limited processing power |
Cost-effective | Restricted memory |
Low power consumption | Limited user interface options |
Real-time processing | Device-specific constraints |
Easy to program | Environmental vulnerability |
FAQS
1. What are the main advantages of a microcontroller?
Microcontrollers are compact, cost-effective, and energy efficient devices ideal for real-time processing of computer operations. They are easy to program and easily integrate into a wide range of embedded systems, from household devices to wearable gadgets and are also used in industrial automation.
2. What are the limitations of microcontrollers?
The main limitations include limited processing power, restricted memory, basic user interface capabilities, and vulnerability to environmental conditions like heat and moisture. They are best suited for simple, dedicated tasks rather than complex computing.
3. How does a microcontroller differ from a microprocessor?
A microcontroller integrates a processor, memory, and Input & output ports into a single chip, optimized for specific control operations. In contrast, a microprocessor focuses on high-speed computing and typically requires external memory and peripherals to function.
4. Can microcontrollers be used for real-time applications?
Yes, microcontrollers are highly suitable for real-time applications because they can quickly respond to external events, making them essential in systems like medical devices, automotive controls, and industrial machines.
Conclusion
Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of microcontrollers is essential when selecting the right component for your project. Microcontrollers offer a compact size, affordable, and energy-efficient solution for countless computer applications.
However, their limited processing power, memory, and flexibility mean they may not be suitable for every situation.
By knowing both the strengths and weaknesses of microcontrollers, you can make informed decisions that lead to successful, efficient designs.