Hello Learners, Today we will learn What are the parts of CPU?
In this post, I will explain the different parts of a CPU (Central Processing Unit).
This Article is Best on the whole internet.
If you read this article carefully you will understand all about the internal and external components and parts of CPU.
I Guarantee you, after reading this article you will not need to read any other Articles. In fact, our readers are satisfied with this blog post.
What is CPU?

Picture of CPU
The full name of the computer CPU is Central Processing Unit. CPU is also known as a processor. A CPU is also called the brain of a computer system.
A computer CPU is an electronic microchip or Microprocessor that performs processing based on the instructions given to the data by the user.
CPU is the main part of a computer system without which the computer system cannot process any instruction. The processor has many functions in a computer system.
I hope you understand Computer CPU.
Read Also - Learn What is CPU in detail with an explanation.
What are the Parts of CPU?
There are many such parts of a computer CPU, but mainly the Central Processing Unit has only three parts.
Which have many main functions in the computer of these three parts. Which I will tell in detail in this post
There are three main parts of CPU ( Central Processing Unit ), which are given below.
- ALU
- CU
- Memory or Storage Unit
These all are internal parts of the CPU.
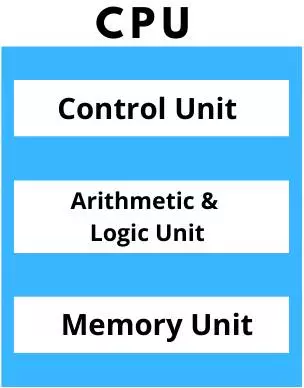
Picture of Parts of CPU
Read Basic Fundamental of Computer System
- What is Computer?
- What is CPU?
- What is Software?
- Components of Computer System
- Hardware Components of Computer
- Parts of Computer
- Generations of Computer
- Classifications of Computer
- Applications of Computer
- Uses of Computer System
- Functions of Computer
- Uses of Computer Graphics
- Uses of Internet
- Uses of Smartphones
- Uses of Mobile Phone
- Uses of Laptop
- Types of Laptop
- Different Types of Computer
- Types of Web Browser
- Block Diagram of Computer
- Advantages of Computer
- Disadvantages of Computer
- Characteristics of Computer
- Limitations of Computer
- Capabilities of Computer
- Elements of Computer System
- Structure of Computer
- Names of Computer
- Operations of Computer
- What is Accuracy in Computer ?
- What is Speed in computer?
- Types of Operating System
- What is Pen Drive?
- What is Portable Computer and its types?
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Internet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Mobile Phone
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Email
- Examples of Hardware
- Examples of Utility Software
- Examples of Web Applications
- Parts of Keyboard
- Parts of Mouse
1. Arithmetic and Logical Unit (ALU)
The arithmetic and logical unit (ALU) is a fundamental component in all computers that performs arithmetic and logic operations.
The ALU is used for addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, comparison of two numbers, and Boolean operations.
It does not handle instruction sequencing or directly deals with memory.
The ALU has some major advantages over the CPU because it only needs to be designed for one type of task instead of many.
An advantage of the CPU is that it can work more on instruction sequencing.
Every computer has an ALU but how it functions can vary from machine to machine.
One of the most important things about the design of an ALU is its size.
A small ALU will give you faster results but will not always give you accurate results while a larger one will be slower but more accurate.
What are the Functions of ALU?
There are various functions of Arithmetic and logic unit, which are given below.
- The ALU performs calculations and is capable of takes logical decisions.
- Arithmetic and Logic Unit used to make decisions like performing arithmetic and logical operations on the computer.
- ALU is like a bridge between the computer’s primary memory and the secondary memory. All the data and instructions that are exchanged between the primary and secondary memory pass through the Arithmetic and Logic Unit ( ALU ).
2. Control Unit (CU)
The control unit (CU) is the part of a computer that controls what happens inside it.
It is like the brain of a computer, making decisions and controlling what goes on inside the machine.
The CU reads the instructions that are stored in its memory and sends out electrical signals to each component of the computer, telling them what to do with the data they've been given.
The control unit has two parts: an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) and a control unit proper.
The ALU is responsible for mathematical calculations, such as adding numbers or performing logical operations, while the control unit directs traffic within the computer so information can be sent to different parts of it quickly.
The control unit is one of the most complex parts of a computer.
It consists of an instruction register, various registers for storing data, an arithmetic logic unit for executing arithmetic operations, and various other circuits to synchronize the other components.
What are the Functions of CU?
There are various functions of control unit, which are given below.
- The control unit controls the order in which instructions move in and out of the processor and so on.
- Control Unit responsible for fetches decodes, and executes the input data, converting it into signal and storing it for further processing.
- Control Unit ( CU ) controls the functioning of other hardware components of the CPU like ALU and Registers.
- Control Unit issues the control signals that control computer hardware.
- The control unit moves the data around the computer system.
3. Memory or Storage Unit
A memory or storage unit in a computer is an electronic device that stores data, programs, and other information.
The two main types of memory are RAM and Hard Drive. RAM stands for Random Access Memory.
It is a volatile type of storage because it requires power to maintain its contents.
It is mostly used for temporarily storing data while the computer is on.
The Hard Drive is non-volatile, meaning it retains stored data even when power isn’t applied to it.
It can be used to store large amounts of data permanently, so it is important for you to back up your files regularly.
Computers provide the ability to store and retrieve data.
Data is stored on a Hard Drive or Memory Unit and can be accessed by programs that are running on the computer.
Memory is typically measured in bytes.
The amount of RAM (Random Access Memory) determines how much data can be accessed at one time.
What are the Functions of Memory Unit?
There are various functions of memory unit, which are given below.
- The primary function of memory is to store data.
- The memory unit store the user instruction.
- The memory unit store the user output.
Components of CPU
CPU stands for Central Processing Unit. It is the "brain" of a computer that can process data and execute instructions.
CPU is an electronic device that measures the progress of a computer program as it executes, providing an important measure of a computer's effectiveness.
There are many different types of CPUs but they all have certain components in common. Here are the components of the CPU in a computer.
There are various components of central processing unit, which are given below.
- Registers
- Cache
- Buses
- CPU Clock
1. Registers
A register is a small amount of high-speed memory. It is connected to the microprocessor and can be accessed much more quickly than any other part of the computer.
There are 8 registers in the CPU, which are designated by their numbers 0-7.
The names for these registers come from adding an "e" to their respective numbers.
Each register has a different use, but they all contribute to the performance of the computer in some way.
There are various types of registers, which are given below.
- MAR Register
- MDR Register
- MBR Register
- PC Register
- Index Register
- Instruction Register
- Accumulator Register
What are the Functions of Register?
There is various function of the register, which are given below.
- In CPU Input registers are used to carry the input data.
- In the CPU Output registers are used to carry the output data.
- The Temporary registers store the temporary data.
- In the CPU, Address registers stored the address of the memory.
- The program counter stores the address of the user instructions.
- In the CPU Data registers hold the memory operand.
- The user instruction, Instruction registers hold the instruction codes.
2. Cache
The cache memory in a computer is the fastest memory that the CPU can access.
The CPU has to talk to the main memory in order to get what it needs, but this takes a lot of time.
So when the CPU asks for something, the cache checks if it has it and saves some time.
If not, then the CPU has to go back to the main memory and check again.
Caches are designed specifically for speed and efficiency, which means they work on a separate bus from other parts of the system.
When you turn on your computer and boot up your operating system, for instance, your CPU will be reading data from different parts of your hard drive into its cache so that it can access them more quickly later on.
The cache is generally divided into two sections: Level 1 (L1) and Level 2 (L2).
An L1 cache generally contains instructions or data that was recently used by an earlier process executed by the CPU; while an L2 cache generally stores.
What are the functions of Cache?
There are various functions of cache in the CPU, which are given below.
- Cache memory reduces the amount of time needed to fetch and execute the instructions.
- Cache memory stores data temporarily for later use.
3. Buses
These days, the term “bus” often refers to a vehicle that carries passengers.
However, in the computing world, buses are about data, not people. A bus is a common pathway that connects many different components of your computer.
It is sometimes called a motherboard or chipset. Data travels across these pathways at very high speeds.
The more channels there are for data to travel, the faster it can move around the computer.
It’s basically how data is passed between the different parts of your computer.
The type of bus that you get will determine how fast your computer will run, and it will also affect how much memory you can use.
There are three types of the bus are used in the central processing unit (CPU), Which names are given below.
- Address Bus
- Data Bus
- Control Bus
What are the Functions of Bus?
There are various functions of a bus, which are given below.
- A bus is used to share data between different devices.
- A bus supplies the electric power to different components of the computer system.
4. CPU Clock
The clock is the heartbeat of your computer. It's what lets you know how long it's been since the last refresh on your screen.
It's also what tells your computer when to load up an app or file, and when to do calculations.
Every program on your computer has a set time for processing, and the clock determines how often it gets to process data.
Here are some things that make up the CPU clock-
- The number of pulses per second (Hertz).
- The percentage of these pulses that are "on" versus "off" (duty cycle).
- The time in milliseconds between each on the pulse (period).
The right settings for these three components determine how long it will take for one instruction to process through your processor.
When you're building a new system, it's important to know what kind of power supply you need, even before you decide which CPU is best for you.
If you don't have enough power from the power supply.
What are the Functions of CPU Clock?
There are different functions of the CPU clock, which are given below.
- The clock maintains the synchronization of the components of a computer system.
- A CPU clock keeps track of the current date and time.
What are the Types of Computer CPU?
There are various types of computer CPU, which are given below.
- Single-core CPU
- Dual-core CPU
- Quad-core CPU
- Hexa Core processors
- Octa-core processors
- Deca-core processor
What are the Features of CPU?
There are various features of central processing unit, which are given below.
- Cache Memory
- Cores in CPU
- Speeds
- Bandwidth
- Hyper-Threading
- Virtualization Help
- Architecture of CPU
- Embedded GPU
What are the Functions of CPU?
There are four functions of central processing unit ( CPU ), which are given below.
- Fetch
- Decode
- Execute
- Store
FAQ Related to Part of CPU
1. How Many parts of CPU?
There are seven ( 7 ) parts of a Computer CPU.
2. What are the internal parts of CPU?
There are various internal parts of CPU (Central Processing Unit), which are given below.
- ALU
- CU
- Storage Unit
- Registers
- Cache
- Buses
- CPU Clock
3. What are main parts of CPU?
There are three main parts of CPU, which are given below.
4. What are the 5 parts of CPU?
The 5 parts of CPU, which are given below.
- ALU
- CU
- Storage Unit
- Registers
- Cache
We hope that you have fully understood about components and parts of CPU, if you still have not understood, then please comment on us.
If you liked this article, then you can share this post.
It is very simple &lucid language easy to understand……thanks sir
Welcome Vijay Deshmukh
I have like the website… It makes someone understand fully and easily well done..
Thanks Suzan
This is amazing these notes has helped me to understand what to deliver to my pupils in class in computer studies
Thanks, Mwiche Namwila
It is usefull to increase knowledge, nice to read.
Thanks, Yohan
Welcome Daisywin
This note have help me a lot. Thanks
Wow
Very helpful indeed reminds me of ICT in college