Everyone will know about a computer but no one knows the full form of computer.
Often the computer full form is asked in your school and college.
After all, What is the full form of computer?
So let's know about the full form of computer and about the What is Computer?
In this post, I will explain in detail all full form of computer parts and Computer Related Full Forms.
This Article is Best on the whole internet.
If you read this article carefully you will understand all A to Z Full Form Computer.
I Guaranteed you, after reading this article you will not need to read any other Articles. In fact, our reader’s satisfy in this blog post.What is the Full Form of Computer?
The full form of computer in English language.
The Full-Form of computer is Commonly Operated Machine Particular Used For Trade Education Research.
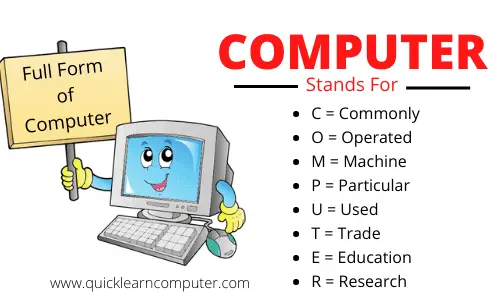
Picture of Full Form of Computer
To understand you, the complete full form of each word of the Computer is given in the table below.
C | Commonly |
O | Operated |
M | Machine |
P | Particular |
U | Used |
T | Trade |
E | Education |
R | Research |
This computer full form is very common and popular full form that will be taught in your school and college.
Suggested Video of Computer full form.
What is the Meaning of Computer?
In this post, I will explain meaning of every word of computer in detail.
C for Commonly ( What is Commonly in computer? )
This usually means that any common person can use it.
For example, children, men, women can use any computer.
O for Operated ( What is Operated in computer? )
This means that any normal person can operate this device very easily.
For example, children can also operate computers very easily.
M for Machine ( What is Machine in computer? )
This means that a computer is an electronic machine.
A computer cannot function without electricity.
A computer is a machine that makes the work of humans very easily and quickly.
P for Particular ( What is Particular in computer?)
Particular has no meaning. Particular is an adjective word.
This word is used to denote a special thing.
U for Used ( What is Used? )
You all will know that 'used' means 'use'.
This means that you can use a computer. Used is an adjective word.
T for Trade ( What is Trade in computer? )
The term trade is used in trade. This means that moving a service from one place to another and selling and buying that service is called trade.
Trade in computers means exchanging data from one place to another.
E for Education ( What is Education in computer? )
Education means in computers that computers are widely used in the field of education.
R for Research ( What is Research in computer? )
Research is a creative thing. Increase collections of knowledge are called research.
Today scientists are doing a lot of research with the help of computers.
What is the long form of computer?
There are many other long full forms of such computers, let us know about all of them as well.
These are all computer full forms.
- Common Operation Made Possible Under Technical Engineering Researches.
- Commonly Operating Machine Particular Used For Technical And Education Research.
- Common Operating Machine Particularly Used For Technical and Educational Research.
- Common Operating Machine Particularly Used For Trade Education and Research.
- Common Operating Machine Particularly Used For Training Education and Reporting.
- Computing Oriented Manipulation Programming Used In Technology Education and Research.
- Commonly Oriented Machine Particularly Used For Trade Education and Research.
- Common Oriented Machine Purely Used For Technical and Educational Research.
- Commonly Operating Machine Particular Used For Technical Education And Research.
- Cable of Making Perfectly Uncomplicated Tasks Extremely Rigorous.
- Complicated Office Machine Put Under Tremendous Effort To Reduce Manpower.
- Calculate Operate Memory Print Update Tabulate Edit Response.
- Common Operating Machine Purposely Used For Technological and Educational Research.
What is Computer?
A computer is an electronic and programming machine and device. A computer is a device that works on the instruction of the user.
The computer takes data from the user and by processing that data, the computer gives us the result.
The computer is capable of doing all kinds of work. A computer cannot function without a user. A computer is a type of mathematical machine.
A to Z Full Form of Computer Related Words
Now we are going to tell you about another important full form related to the computer, all this full form is very important for your every exam which you must remember.
| No. | Abbreviation | Full-Form |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | RAM | Random Access Memory |
| 2 | ROM | Read Only Memory |
| 3 | CPU | Central Processing Unit |
| 4 | URL | Uniform Resource Locator |
| 5 | USB | Universal Serial Bus |
| 6 | VIRUS | Vital Information Resource Under Siege |
| 7 | TCP | Transmission Control Protocol |
| 8 | UPS | Uninterruptible Power Supply |
| 9 | SATA | Serial Advanced Technology Attachment |
| 10 | PSU | Power Supply Unit |
| 11 | SMPS | Switched-Mode Power Supply |
| 12 | CD | Compact Disc |
| 13 | DVD | Digital Versatile Disc |
| 14 | CRT | Cathode Ray Tube |
| 15 | DEC | Digital Equipment Corporation |
| 16 | SAP | System Application and Products |
| 17 | PNG | Portable Network Graphics |
| 18 | IP | Internet Protocol |
| 19 | GIS | Geographical Information system |
| 20 | DDS | Digital Data Storage |
| 21 | CAD | Computer Aided Design |
| 22 | ACPI | Advanced Configuration and Power Interface |
| 23 | AGP | Accelerated Graphics Port |
| 24 | APM | Advanced Power Management |
| 25 | APIPA | Automatic Private Internet Protocol Addressing |
| 26 | HTTP | Hyper Text Transfer Protocol |
| 27 | HTTPS | Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secure |
| 28 | GPU | Graphics Processing Unit |
| 29 | GDI | Graphics Device Interface |
| 30 | ICP | Internet Cache Protocol |
| 31 | GIGO | Garbage In Garbage Out |
| 32 | GMAIL | Graphical Mail |
| 33 | CAN | Campus Area Network |
| 34 | CAL | Computer Aided Leering |
| 35 | GPL | General Public License |
| 36 | GCR | Group Code Recording |
| 37 | MSN | Microsoft Networks |
| 38 | BCC | Blind Carbon Copy |
| 39 | VDI | Virtual Desktop Infrastructure |
| 40 | MPEG | Moving Picture Experts Group |
| 41 | TPU | Tensor Processing Unit |
| 42 | PSD | Photoshop Document |
| 43 | DPI | Dots Per Inch |
| 44 | FYA | For Your Action |
| 45 | CRS | Computer Reservation System |
| 46 | BFD | Binary File Descriptor |
| 47 | ABR | Available Bit Rate |
| 48 | GBPS | Gigabits Per Second |
| 49 | PING | Packet InterNet Groper |
| 50 | CSMA | Carrier Sense Multiple Access |
| 51 | AD | Active Directory |
| 52 | ADC | Analog to Digital Converter |
| 53 | BGP | Border Gateway Protocol |
| 54 | CSI | Common System Interface |
| 55 | DHCP | Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol |
| 56 | OSI | Open Systems Interconnection |
| 57 | LAN | Local Area Network |
| 58 | WAN | Wide Area Network |
| 59 | MAN | Metropolitan Area Network |
| 60 | PAN | Personal Area Network |
| 61 | MAC | Media Access Control |
| 62 | OMR | Optical Mark Recognition |
| 63 | NIC | Network Interface Card |
| 64 | LDAP | Lightweight Directory Access Protocol |
| 65 | UART | Universal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter |
| 66 | DCE | Distributed Computing Environment |
| 67 | PFA | Please Find Attached |
| 68 | HCI | Human Computer Interaction |
| 69 | FHS | Filesystem Hierarchy Standard |
| 70 | FCS | Frame Check Sequence |
| 71 | DVE | Digital Video Effects |
| 72 | DLL | Data Link Layer |
| 73 | CSV | Comma Separated Values |
| 74 | CTCP | Client–to–Client Protocol |
| 75 | ABI | Application Binary Interface |
| 76 | MIS | Management Information System |
| 77 | BIOS | Basic Input Output System |
| 78 | SMTP | Simple Mail Transfer Protocol |
| 79 | LTE | Long Term Evolution |
| 80 | AHA | Accelerated Hub Architecture |
| 81 | ALU | Arithmetic Logical Unit |
| 82 | FPU | Floating Point Unit |
| 83 | FXP | File Exchange Protocol |
| 84 | HID | Human Interface Device |
| 85 | IOS | iPhone Operating System |
| 86 | PATA | Parallel Advanced Technology Attachment |
| 87 | DDR | Double Data Rate |
| 88 | DFS | Distributed File System |
| 89 | MIPS | Million Instructions Per Second |
| 90 | MMC | Microsoft Management Console |
| 91 | VGCT | Video Graphics Character Table |
| 92 | WBMP | Wireless BitMap Image |
| 93 | PCM | Pulse-Code Modulation |
| 94 | WMA | Windows Media Audio |
| 95 | RAS | Remote Access Service |
| 96 | HTM | Hierarchical Temporal Memory |
| 97 | SIS | Security and Intelligence Services |
| 98 | LBA | Logical Block Addressing |
| 99 | CIDR | Classless Inter-Domain Routing |
| 100 | MIMO | Multiple-Input Multiple Output |
| 101 | PLC | Programmable Logic Controller |
| 102 | SCSI | Small Computer System Interface |
| 103 | NVRAM | Non-Volatile Random-Access Memory |
| 104 | BLOB | Binary large Object |
| 105 | VPN | Virtual Private Network |
| 106 | SFF | Small Form Factor |
| 107 | CAI | Computer–Aided Instruction |
| 108 | EMP | Electro-Magnetic Pulse |
| 109 | EIDE | Enhanced Integrated Drive Electronics |
| 110 | AAC | Advanced Audio Codec |
| 111 | IIOP | Internet Inter-ORB Protocol |
| 112 | ASL | Age Sex Location |
| 113 | MBSA | Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer |
| 114 | ZIP | Zig-zag In-line Package |
| 115 | HSPA | High Speed Packet Access |
| 116 | VFS | Virtual File System |
| 117 | SIMD | Single Instruction Multiple Data |
| 118 | IPC | Inter-Process Communication |
| 119 | DAC | Discretionary Access Control |
| 120 | DKIM | Domain Keys Identified Mail |
| 121 | WIFI | Wireless Fidelity |
| 122 | PTP | Picture Transfer Protocol |
| 123 | IGRP | Interior Gateway Routing Protocol |
| 124 | HIG | Human Interface Guidelines |
| 125 | UNIVAC | Universal Automatic Computer |
| 126 | CIFS | Common Internet File System |
| 127 | HAL | Hardware Abstraction Layer |
| 128 | IPV6 | Internet Protocol Version 6 |
| 129 | CNR | Communication Network Riser |
| 130 | EISA | Extended Industry Standard Architecture |
| 131 | RPM | Red-Hat Package Manager |
| 132 | DLT | Distributed Ledger Technology |
| 133 | ISH | Information Super Highway |
| 134 | BY | Bronto-bytes |
| 135 | DTS | Digital Theater System |
| 136 | MSB | Most Significant Bit |
| 137 | HVD | Holographic Versatile Disk |
| 138 | MOSFET | Metal-Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor |
| 139 | AMR | Adaptive Multi-Rate |
| 140 | CMD | Command |
| 141 | BCD | Binary Coded Decimal |
| 142 | DMA | Direct Memory Access |
| 143 | EB | Exa-bytes |
| 144 | AVI | Audio Video Interleave |
| 145 | WLAN | Wireless Local Area Network |
| 146 | CAM | Computer Aided Manufacturing |
| 147 | RIFF | Resource Interchange File Format |
| 148 | TFTP | Trivial File Transfer Protocol |
| 149 | WUSB | Wireless Universal Serial Bus |
| 150 | HHD | Hybrid Hard Drive |
| 151 | HSDPA | High Speed Downlink Packet Access |
| 152 | AST | Abstract Syntax Tree |
| 153 | MSD | Most significant Digit |
| 154 | IRQ | Interrupt Request |
| 155 | DVI | Digital Visual Interface |
| 156 | SPARC | Scalable Processor Architecture |
| 157 | URI | Uniform Resource Identifier |
| 158 | EPROM | Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory |
| 159 | SAN | Storage Area Network |
| 160 | EBCDIC | Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code |
| 161 | MVS | Multiple Vendor System |
| 162 | NAS | Network Attached Storage |
| 163 | BPS | Bits Per Second |
| 164 | LPX | Low Profile Extension |
| 165 | HCL | Hardware Compatibility List |
| 166 | RTS | Real Time Streaming |
| 167 | RAID | Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks |
| 168 | MUI | Multilingual User Interface |
| 169 | MFD | Multi-Function Device |
| 170 | CISC | Complex Instruction Set Computer |
| 171 | MBR | Master Boot Record |
| 172 | BINAC | Binary Automatic Computer |
| 173 | SGRAM | Synchronous Graphics Random Access Memory |
| 174 | DLP | Digital Light Processing |
| 175 | UEFI | Unified Extensible Firmware Interface |
| 176 | LLC | Logical Link Control |
| 177 | DOC | Document (Microsoft Corporation) |
| 178 | ARPANET | Advanced Research Projects Agency Network |
| 179 | ACL | Access Control List |
| 180 | RAIT | Redundant Array of Inexpensive Tapes |
| 181 | MMX | Multi-Media Extensions |
| 182 | STP | Spanning Tree Protocol |
| 183 | MLI | Multiple Link Interface |
| 184 | RIP | Routing Information Protocol |
| 185 | AIFF | Audio Interchange File Format |
| 186 | RMA | Returned Materials Authorization |
| 187 | EGP | Exterior Gateway Protocol |
| 188 | XMF | Extensible Music File |
| 189 | MTBF | Mean Time Between Failure |
| 190 | MIME | Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions |
| 191 | SRAM | Static Random-Access Memory |
| 192 | SDR | Software-Defined Radio |
| 193 | PAP | Password Authentication Protocol |
| 194 | VRAM | Video Random Access Memory |
| 195 | WAP | Wireless Application Protocol |
| 196 | TGT | Ticket Granting Ticket |
| 197 | GIF | Graphics Interchange Format |
| 198 | TPM | Trusted Platform Module |
| 199 | SPSS | Statistical Package for the Social Sciences |
| 200 | ULSI | Ultra Large-Scale Integration |
| 201 | EIGRP | Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol |
| 202 | CDN | Content Delivery Network |
| 203 | NMI | Non-Maskable Interrupt |
| 204 | PPI | Pixels Per Inch |
| 205 | RJ45 | Registered Jack 45 |
| 206 | SEC | Single Edge Connector |
| 207 | BER | Bit Error Rate |
| 208 | OOPS | Object-Oriented Programming System |
| 209 | ATA | Advanced Technology Attachment |
| 210 | RISC | Reduced Instruction Set Computer |
| 211 | NFS | Network File System |
| 212 | SFC | System File Checker |
| 213 | ICR | Intelligent Character Recognition |
| 214 | BTX | Balanced Technology Extended |
| 215 | DOS | Disk Operating System |
| 216 | CTS | Clear to Send |
| 217 | AMD | Advanced Micro Devices |
| 218 | DVD | Digital Video Disc |
| 219 | CD-R | Compact Disk – Recordable. |
| 220 | BAL | Basic Assembly Language |
| 221 | UTF | Unicode Transformation Format |
| 222 | MIDI | Musical Instrument Digital Interface |
| 223 | BAT | Microsoft Batch Processing |
| 224 | VT | Video Terminal |
| 225 | HP | Hewlett Packard |
| 226 | URN | Uniform Resource Name |
| 227 | D2D | Device to Device |
| 228 | DSHD | Double Sided High Density |
| 229 | FDC | Floppy Disk Controller |
| 230 | SDN | Service Delivery Network |
| 231 | SBU | Standard Build Unit |
| 232 | MPL | Mozilla Public License |
| 233 | ENIAC | Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer |
| 234 | CAQA | Computer–Aided Quality Assurance |
| 235 | ASF | Advanced Systems Format |
| 236 | VM | Virtual Machine |
| 237 | Mac | Macintosh |
| 238 | OS | Operating System |
| 239 | MNG | Multiple-image Network Graphics |
| 240 | CD-ROM | Compact Disk-Read Only Memory |
| 241 | MSB | Most Significant Byte |
| 242 | TCP/IP | Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol |
| 243 | DMI | Desktop Management Interface |
| 244 | NTP | Network Time Protocol |
| 245 | PINE | Program for Internet News and Email |
| 246 | SSL | Secure Sockets Layer |
| 247 | BCR | Bar Code Reader |
| 248 | SPI | Serial Peripheral Interface |
| 249 | KBPS | Kilobits Per Second |
| 250 | TSI | Time Slot Interchange |
| 251 | ABC | Atanasoff-Berry Computer |
| 252 | YB | Yotta Byte |
| 253 | ZB | Zetta-bytes |
| 254 | WDDM | Windows Display Driver Model |
| 255 | ZIF | Zero-Insertion-Force |
| 256 | RDBMS | Relation Database Management System |
| 257 | MSI | Microsoft Installer |
| 258 | ISP | Internet Service Provider |
| 259 | WAV | Waveform Audio |
| 260 | TPS | Transaction Per Second |
| 261 | ISV | Independent Software Vendor |
| 262 | SXGA | Super Extended Graphics Array |
| 263 | GP | Graphics port |
| 264 | BGA | Ball Grid Array |
| 265 | SIS | Safety Instrumented System |
| 266 | CGI | Common Gateway Interface |
| 267 | Portable Document Format | |
| 268 | MMU | Memory Management Unit |
| 269 | PIC | Peripheral Interface Controller |
| 270 | NIU | Network Interface Unit |
| 271 | TPS | Transaction Processing System |
| 272 | VLSI | Very Large-Scale Integration |
| 273 | ESD | Electro Static Discharge |
| 274 | MAPI | Messaging Application Program Interface |
| 275 | KB | Kilo-bytes |
| 276 | DSL | Domain–Specific Language |
| 277 | PB | Peta-bytes |
| 278 | NAP | Network Access Point |
| 279 | MS-DOS | Microsoft Disk Operating System |
| 280 | WMV | Windows Media Video |
| 281 | MFA | Multi-Factor Authentication |
| 282 | GUI | Graphical User Interface |
| 283 | RIS | Remote Installation Service |
| 284 | ASCII | American Standard Code for Information Interchange |
| 285 | ELF | Executable and Linkable Format |
| 286 | WWAN | Wireless Wide Area Network |
| 287 | DFD | Data Flow Diagram |
| 288 | IRC | Internet Relay Chat |
| 289 | PC | Personal Computer |
| 290 | SDL | Software and Documentation Localization |
| 291 | WINS | Windows Internet Name Service |
| 292 | NOS | Network Operating System |
| 293 | UNICS | UNiplexed Information Computing System |
| 294 | DVR | Digital Video Recorder |
| 295 | XMS | Extended Memory Specification |
| 296 | LSI | Large-Scale Integration |
| 297 | STP | Shielded Twisted Pair |
| 298 | PCB | Process Control Block |
| 299 | AGA | Advanced Graphics Architecture |
| 300 | HSUPA | High-Speed Uplink Packet Access |
| 301 | ICS | Internet Connection Sharing |
| 302 | SOA | Service Oriented Architecture |
| 303 | WWW | World Wide Web |
| 304 | DLL | Dynamic Link Library |
| 305 | DAP | Direct Access Protocol |
| 306 | WMF | Windows Metafile |
| 307 | EVDO | Evolution Data Optimized Or Evolution Data Only |
| 308 | FAT | File Allocation Table |
| 309 | DTE | Data Terminal Equipment |
| 310 | PAL | Phase Alternation Line |
| 311 | VGA | Video Graphics Array |
| 312 | HSSI | High-Speed Serial Interface |
| 313 | SIMM | Single In-Line Memory Module |
| 314 | IPX | Internetwork Packet Exchange |
| 315 | BWF | Broadcast Wave Format |
| 316 | CRIMM | Continuity-Rambus Inline Memory Module |
| 317 | OOP | Object Oriented programming |
| 318 | RTOS | Real Time Operating System |
| 319 | DBSN | Database Source Name |
| 320 | IHV | Independent Hardware Vendor |
| 321 | ISR | Interrupt Service Routine |
| 322 | SOAP | Simple Object Access Protocol |
| 323 | FTP | File Transfer Protocol |
| 324 | DRAM | Dynamic Random-Access Memory |
| 325 | BSOD | Blue Screen of Death |
| 326 | HTX | Hyper Transport Expansion |
| 327 | LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| 328 | DIVX | DIgital Video Express |
| 329 | UAC | User Account Control |
| 330 | CASE | Computer-Aided Software Engineering |
| 331 | HDMI | High Definition Multimedia Interface |
| 332 | VDC | Video Display Controller |
| 333 | AVC | Advanced Video Coding |
| 334 | CGA | Color Graphics Array |
| 335 | DPMS | Display Power Management Signaling |
| 336 | DBA | DataBase Administrator |
| 337 | P2P | Peer-To-Peer |
| 338 | MSI | Medium Scale Integration |
| 339 | EPP | Enhanced Parallel Port |
| 340 | EFS | Encrypting File System |
| 341 | MHz | Megahertz |
| 342 | WPAN | Wireless Personal Area Network |
| 343 | CAN | Controller Area Network |
| 344 | VDU | Video Display Unit |
| 345 | JPG | Joint Photographic Expert Group |
| 346 | MB | Mega-bytes |
| 347 | ENI | Elastic Network Interface |
| 348 | VPU | Visual Processing Unit |
| 349 | MTP | Media Transfer Protocol |
| 350 | MDI | Multiple Document Interface |
| 351 | TDR | Time Domain Reflectometer |
| 352 | WUXGA | Wide Ultra Extended Graphics Array |
| 353 | NAP | Network Access Protection |
| 354 | DWM | Desktop Window Manager |
| 355 | ERP | Enterprise Resource Planning |
| 356 | PPT | PowerPoint Presentation |
| 357 | LSB | Least Significant Byte |
| 358 | CCD | Charged Coupled Device |
| 359 | VCR | Video Cassette Recorder |
| 360 | EEPROM | Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory |
| 361 | CRC | Cyclic Redundancy Check |
| 362 | XGA | Extended Graphics Array |
| 363 | LSB | Least Significant Bit |
| 364 | ZISC | Zero Instruction Set Computer |
| 365 | ISA | Instruction Set Architecture |
| 366 | HPC | High-Performance Computing |
| 367 | MSDN | Microsoft Developer Network |
| 368 | BPI | Bytes Per Inch |
| 369 | SVGA | Super Video Graphics Array |
| 370 | RDF | Resource Description Framework |
| 371 | MFP | Multi-Function Product |
| 372 | FCPGA | Flip Chip Pin Grid Array |
| 373 | ASR | Automated System Recovery |
| 374 | VAN | Value-Added Network |
| 375 | PIO | Programmed Input/Output |
| 376 | RGB | Red, Green, Blue |
| 377 | FDMA | Frequency-Division Multiple Access |
| 378 | SWF | Shock Wave Flash |
| 379 | EOF | End of File |
| 380 | POP | Post Office Protocol |
| 381 | CBEMA | Computer Business Equipment Manufacturers Association |
| 382 | GB | Giga-bytes |
| 383 | EDP | Electronic Data Processing |
| 384 | DIMM | Dual In-Line Memory Module |
| 385 | VM | Virtual Memory |
| 386 | SHDSL | Single-pair High-speed Digital Subscriber Line |
| 387 | WEP | Wired Equivalent Privacy |
| 388 | MBCS | Multi Byte Character Set |
| 389 | IPV4 | Internet Protocol Version 4 |
| 390 | MCR | Multivariant Curve Resolution |
| 391 | MTA | Mail Transfer Agent |
| 392 | BOSS | Bharat Operating System Solutions |
| 393 | ISC | Internet Storm Center |
| 394 | POST | Power on self-test |
| 395 | DTR | Data Terminal Ready |
| 396 | SMBIOS | System Management BIOS |
| 397 | HPFS | High Performance File System |
| 398 | SNMP | Simple Network Management Protocol |
| 399 | IIS | Internet Information Services |
| 400 | VPG | Virtual Private Gateway |
| 401 | CUA | Common User Access |
| 402 | NID | Network Interface Device |
| 403 | HDD | Hard Disk Drive |
| 404 | IMAP | Internet Message Access Protocol |
| 405 | VLC | Video LAN Client |
| 406 | ERD | Emergency Repair Disk |
| 407 | WPA | Wireless Protected Access |
| 408 | IOS | Internetwork Operating System |
| 409 | PKI | Public key Infrastructure |
| 410 | UDP | User Datagram Protocol |
| 411 | ISA | Industry Standard Architecture |
| 412 | TPDU | Transaction Protocol Data Unit |
| 413 | M3G | Mobile 3D Graphics |
| 414 | DTP | Desktop Publishing |
| 415 | PCI | Peripheral Component Interconnect |
| 416 | CAE | Computer–Aided Engineering |
| 417 | NTFS | New Technology File System |
| 418 | FDD | Floppy Disk Drive |
| 419 | IPP | Internet Printing Protocol |
| 420 | VLAN | Virtual Local Area Network |
| 421 | VXLAN | Virtual Extensible Local Area Network |
| 422 | CTL | Computation Tree Logic |
| 423 | DAT | Digital Audio Tape |
| 424 | BiDi | Bi–Directional |
| 425 | SVG | Scalable Vector Graphics |
| 426 | ECP | Extended Capabilities Port |
| 427 | TB | Tera-bytes |
| 428 | CMOS | Complementary Metal–Oxide–Semiconductor |
| 429 | OCR | Optical Character Reader |
| 430 | JPEG | Joint Photographic Experts Group |
| 431 | SONET | Synchronous Optical Networking |
| 432 | CCS | Common Command Set |
| 433 | CUPS | Common Unix Printing System |
| 434 | ENIAC | Electronic Numerical Integrator and Compute |
| 435 | IVR | Interactive Voice Response |
| 436 | HTPC | Home Theatre Personal Computer |
| 437 | HD | High Definition |
| 438 | EVC | Ethernet Virtual Circuit |
| 439 | NMS | Network Management System |
| 440 | UTP | Unshielded Twisted Pair-Cable |
| 441 | FDDI | Fiber Distributed Data Interface |
| 442 | HAN | Home Area Network |
| 443 | XMPP | Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol |
| 444 | ISCSI | Internet Small Computer Storage Interface |
| 445 | PDP | Plasma Display Panel |
| 446 | VOIP | Voice Over Internet Protocol |
How Many Parts of Computer?

There are many parts of a computer system is given below.
- Monitor
- CPU
- Keyboard
- Mouse
- Storage Unit
- Memory Unit
- UPS
- Motherboard
- Power Supply Unit
- GPU
- Computer Case
- Printer
- Speaker
- Scanner
- Microphone
- Webcam
- Fan
- Sound Card
- CD/DVD Drive
- Power Cord
What are Main Parts of Computer?
There are four main parts of computer system, which are given below.
- Desktop
- CPU
- Keyboard
- Mouse
Desktop - Desktop is a output device. Large-size glass screens are called desktops. The desktop always sits on a wooden desk.
CPU - CPU operates the entire computer system and it is also called the brain of the computer.
Keyboard - The keyboard is an input device in the computer. Which helps the user to input data from the keyboard.
Mouse - The mouse is a pointing device and also an input device. The mouse saves a lot of time of the user.
Basic Components of Computer
There are five basic components of computer System, which are given below.
- Input Unit
- Output Unit
- Memory Unit
- Control Unit
- Arithmetical Logical Unit
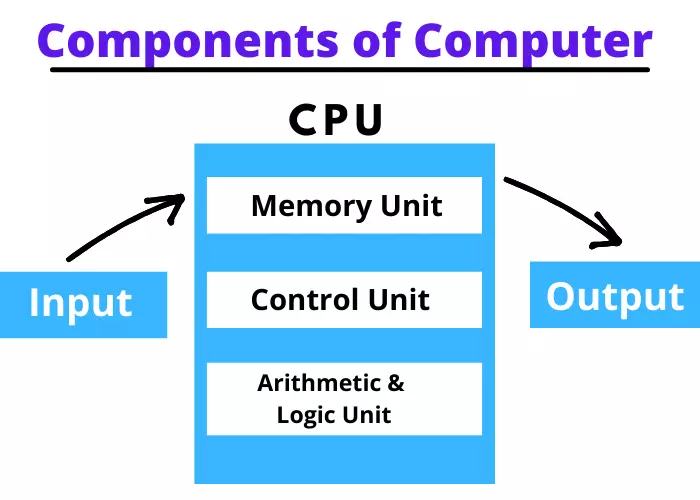
Picture of Components of computer
Advantages of Computer
The computer is capable of doing a variety of tasks at a very fast speed. Today, you can work and also study from home through the computer.
Through the computer, you can talk to online video calls and can also use many types of social media like a - Facebook, YouTube, Instagram and etc.
Today, in the situation like covid 19, in the field of medicine, treatment is being done using computers.

Picture of Advantages of Computer
Disadvantages of Computer
A computer is dependent on the user. A computer consists of an empty box without user. There is a risk of a cyber attack on private data of the computer.
Regular use of computer can also make you sick. Using the computer continuously for long hours can also damage your eye.
Types of Computer
There are three different types of computer.
- Analog Computer
- Digital Computer
- Hybrid Computer

Picture of Types of Computer System
Classification of Computer
The computer is divided into four parts based on its working and size.
- Micro Computer
- Mini Computer
- Mainframe computer
- Super Computer
Generations of Computer
The process of change in the computer from time to time is known as Generations of Computer.
- First Generation of computer
- Second Generation of computer
- Third Generation of computer
- Fourth Generation of computer
- Fifth Generation of computer
Characteristics of Computer
The main characteristics of computer are the following below.
- Speed
- Accuracy
- Diligence
- Reliability
- Versatility
- Storage Capacity
- Automatic
- Quick Decision
- Multitasking
- No Feeling
- Power of Remembering
- No IQ
Limitations of Computer
The work or instruction that a computer is not capable of doing is called Limitations of Computer.
There are some limitations of computer is given below.
- Lack of common-sense
- Zero IQ
- No Feeling
- Computers can’t Decide
- Computers can’t Express their Ideas
- Computers can’t Implement
- Computers can’t Think
Some Famous Computer Brands
There are various computer brands, which names are given below.
- HP
- Lenovo
- MI
- Acer
- DELL
- MacBook by apple
- HCL
Awesome Facts about Computer
- Today 90% of the world's currency is on the computer i.e. 90% of the world's currency is in digital form.
- Do you know that the world's first computer was 18 square feet big and weighed 27 tons.
- The world's first electronic computer was the ENIAC.
- More than 5000 new computer viruses are released every month in the world.
- The world's first 1GB hard disk drive was announced in 1980.
Computer Hardware Related Full Forms
There are various computer hardware related full forms, which are given below.
- CPU - Central Processing Unit
- ROM- Read-only Memory
- RAM - Random Access Memory
- Prom- Programmable Read-Only Memory
- FDD- Floppy Disk Drive
- HDD- Hard Disk Drive
- CD- Compact Disk
- DVD- Digital Video Disk
- BIOS- Basic Input Output System
- SMPS- Switch Mode Power Supply
- VDU- Visual Display Unit
- LED- Light Emitting Diode
- LCD - Liquid Crystal Display
- USB - Universal Serial Bus
- HDMI - High Definition Multimedia Interface
- SSD- Solid State Drive
- VGA- Video Graphics Array
- UPS- Uninterrupted Power Supply
- NTFS- New Technology File System
- MMC- Multi-Media Card
Computer Software Related Full Forms
There are various computer software related full forms, which are given below.
- OS- Operating System
- VIRUS – Vital Information Resources Under Seize
- DVI- Digital Visual Interface
Computer Storage Related Full Forms
There are various computer storage related full forms, which are given below.
- KB - Kilobyte
- MB- Megabyte
- GB- Gigabyte
- TB- Terabyte
- PB- Petabyte
- EB- Exabyte
- ZB- Zetabyte
Computer Networking Related Full Forms
There are various computer networking related full forms, which are given below.
- WIFI- Wireless Fidelity
- WAN- Wide Area Network
- WLAN- Wireless Local Area Network
- DNS- Domain Name System
- HTML- Hyper Text Markup language
- IP- Internet Protocol
- ISP- Internet Service Provider
- VPS- Virtual Private Server
- URL- Uniform Resource Locator
- GSM- Global System for Mobile Communication
- CDMA - Code Division Multiple Access
- SIM- Subscriber Identity Module
- WWW- World Wide Web
- GPRS- General Packet Radio Service
FAQ Related to Computer Full Form
What is the full form of 2-d in computer science?
The Full Form of 2-d in computer science is Two-Dimensional.
U D computer course full form.
U D means Undergraduate Diploma course in computer. Some Popular Diploma course is given below.
- DCA
- ADCA
- CCC
What is the full form of MS excellence in computer?
MS Excellence means MS Excel in computer. The full form of MS Excel is Micro Soft Excel.
Read Other Related Articles
I know my readers love this article.
If you any doubts in this article please check out contact us page.
I Hope you Understand Full Form of Computer. Share this post and mention your comment.
Very informative…good job.
Thanks Suzette
Very educative and informative. thumb up
Thanks Joan Gigin
hi, iam astudent as learning computer science.my full name for fisrt name is Evariste and my last name is Bapfekurera.iam pure africain.me,I need your help.my whatsapp number is 0790906327.
This post will help the internet users for building up new
blog or even a weblog from start to end.
Hello to all, the contents existing at this web page are actually amazing for people
knowledge, well, keep up the nice work fellows.